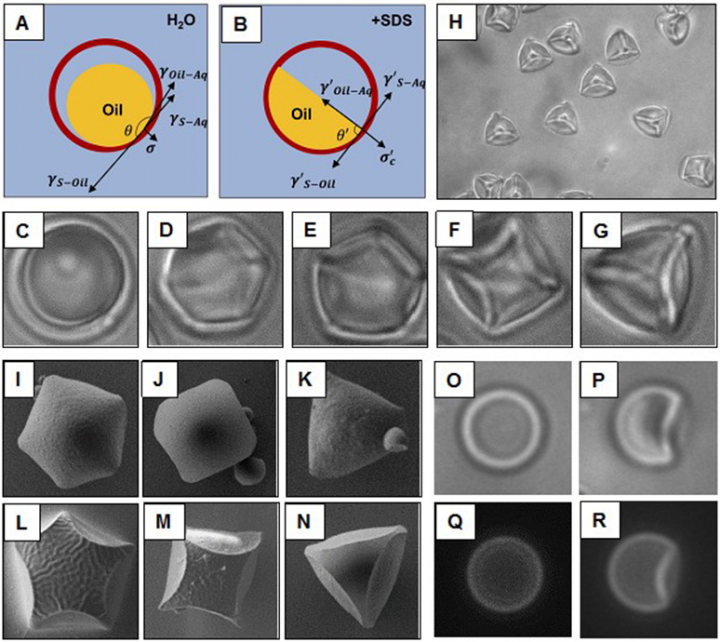
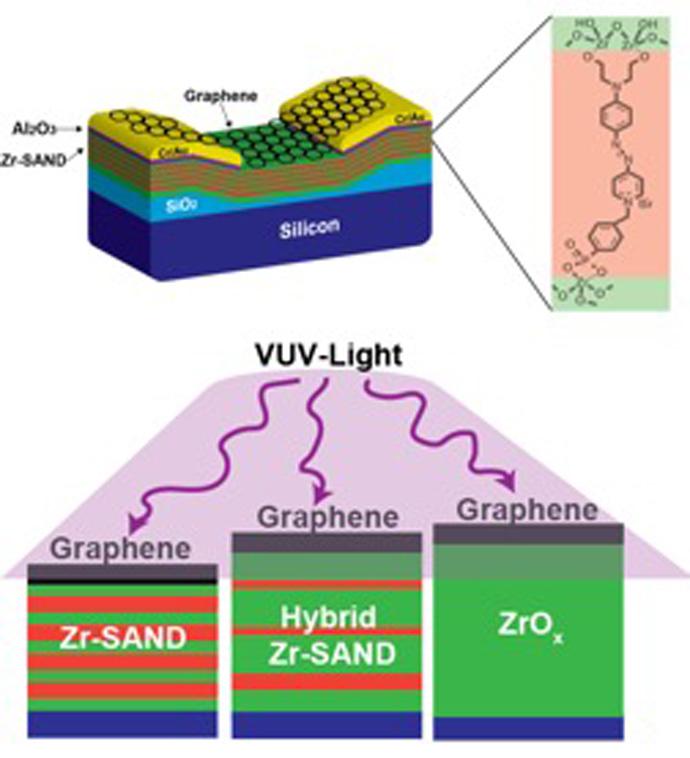
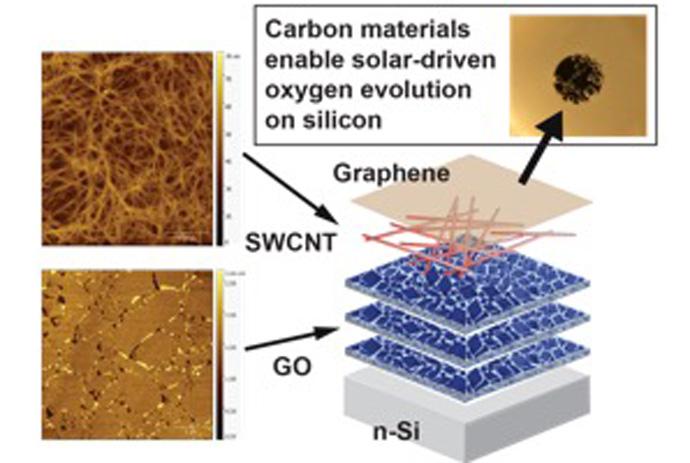
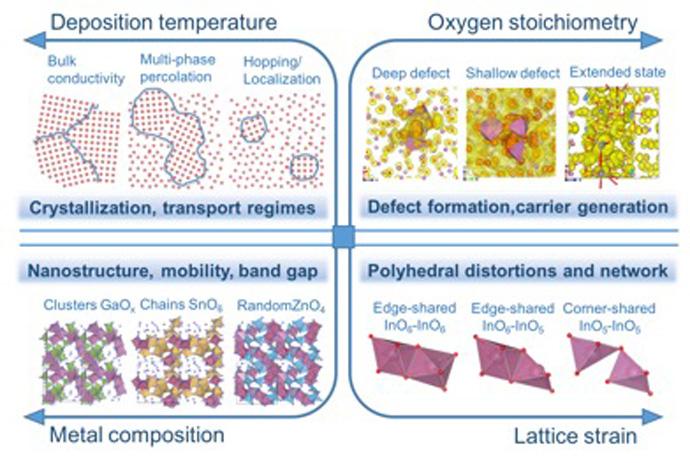
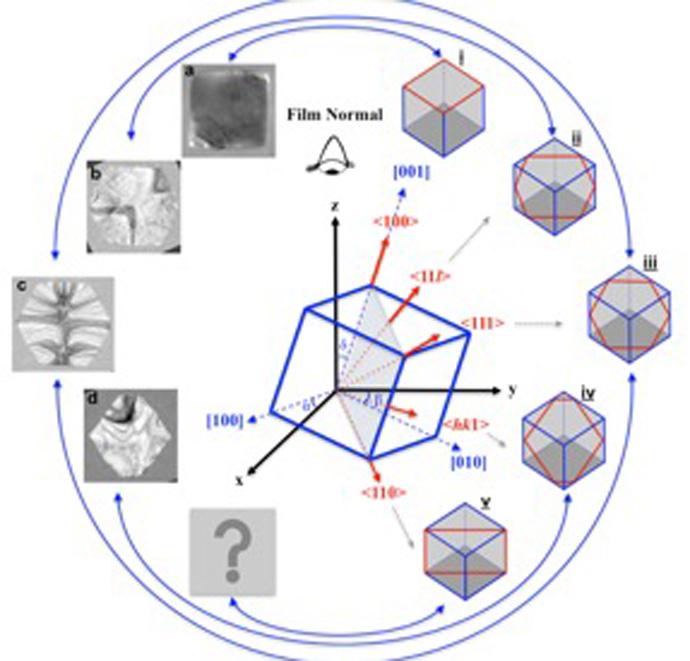
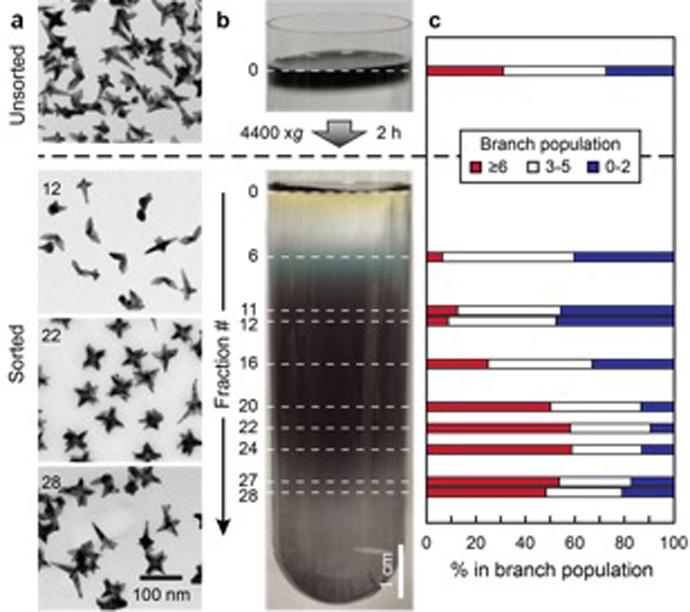
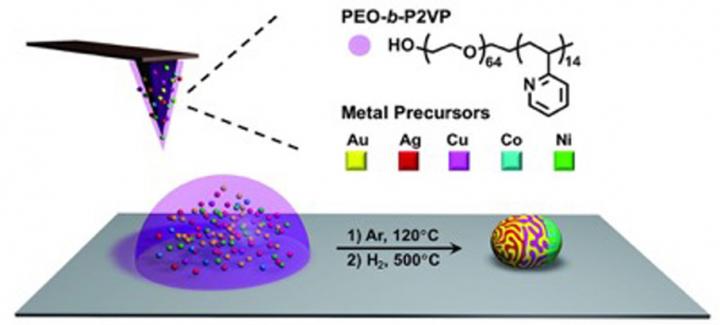
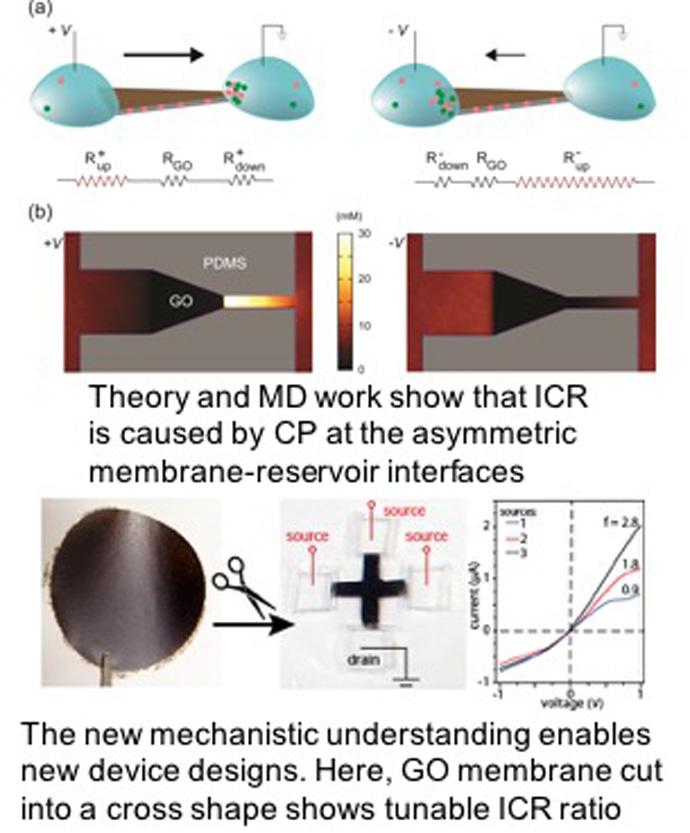
Over the course of two days, the Wisconsin MRSEC presented exciting hands-on, research-inspired materials science activities to over 1500 people during the 2016 Wisconsin Science Festival. The 2016 Wisconsin Science Festival was the largest ever with over 250 events in 20 communities across Wisconsin.