Highlights
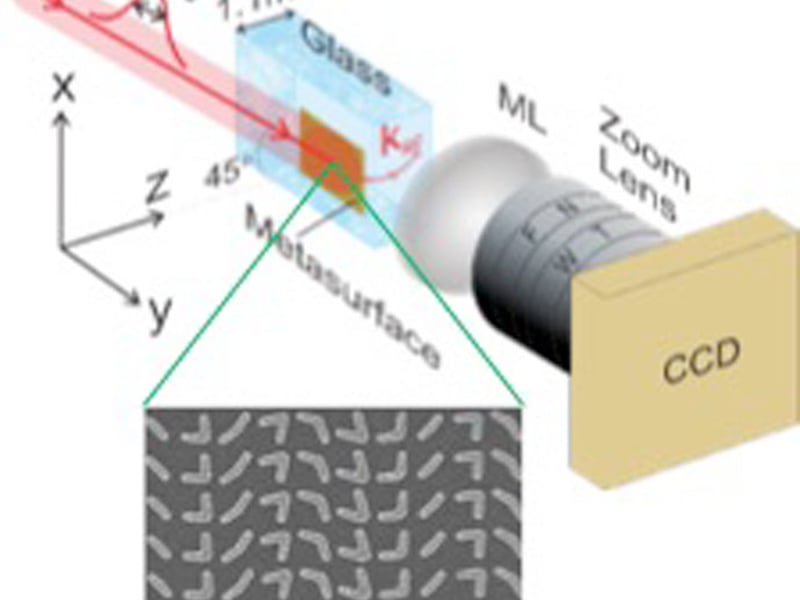
Metasurface Generation of Accelerating Light
M. Henstridge1, C. Pfeiffer2, D. Wang3, A. Boltasseva3, V. Shalaev3, A. Grbic2, and R. Merlin1 1Department of Physics, University of Michigan 2Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Michigan 3School of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Birck Nanotechnology Center, Purdue University
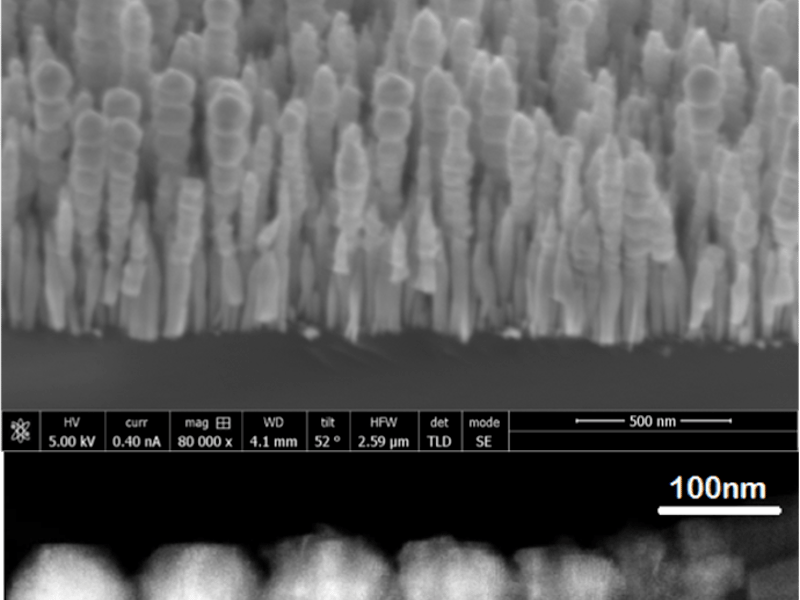
A III-Nitride Monolithic Nanowire Laser for Silicon Photonics
Pallab Bhattacharya1, Joanna Millunchick2, Arnab Hazari1, and Lifan Yan2 1EECS Department, 2MSE Department, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
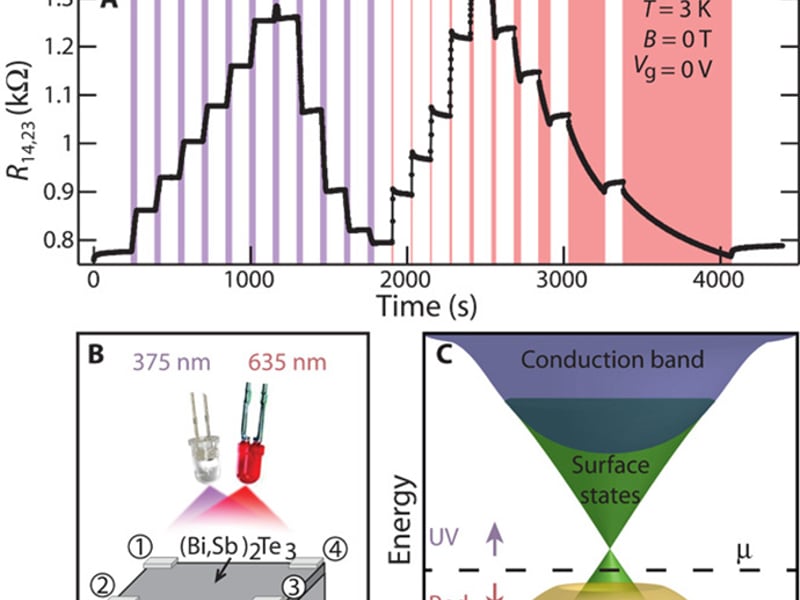
Persistent Optical Gating of a Topological Insulator
Andrew L. Yeats [University of Chicago; University of CA Santa Barbara] Yu Pan [Pennsylvania State University] Anthony Richardella [Pennsylvania State University] Peter J. Mintun [University of Chicago] Nitin Samarth [Pennsylvania State University] David D. Awschalom [University of Chicago; University of CA Santa Barbara]
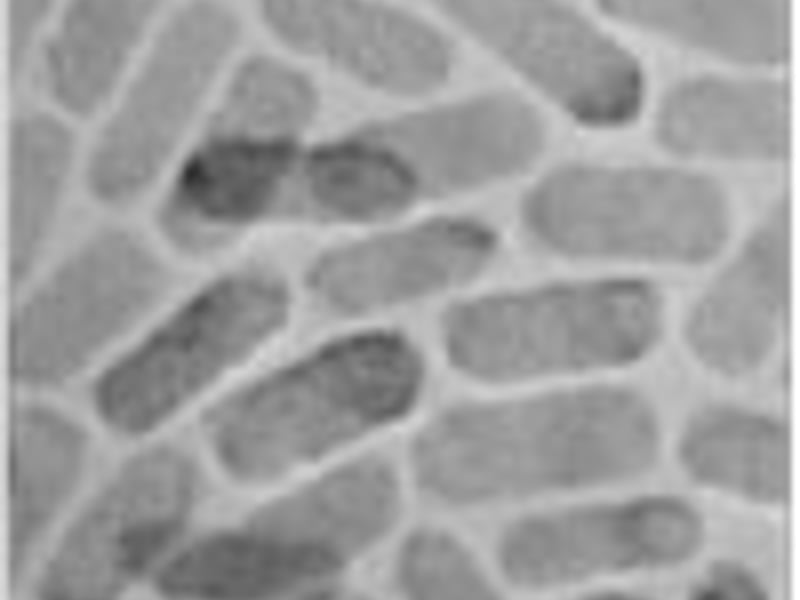
Red, Yellow, Green, and Blue Lasing Using Colloidal Quantum Wells
Chunxing She [University of Chicago] Igor Fedin [University of Chicago] Dmitriy S. Dolzhnikov [University of Chicago] Peter D. Dahlberg [University of Chicago] Gregory S. Engel [University of Chicago] Richard D. Schaller [Argonne National Lab/ Northwestern University] Dmitri V. Talapin [University of Chicago/ Argonne National Lab]
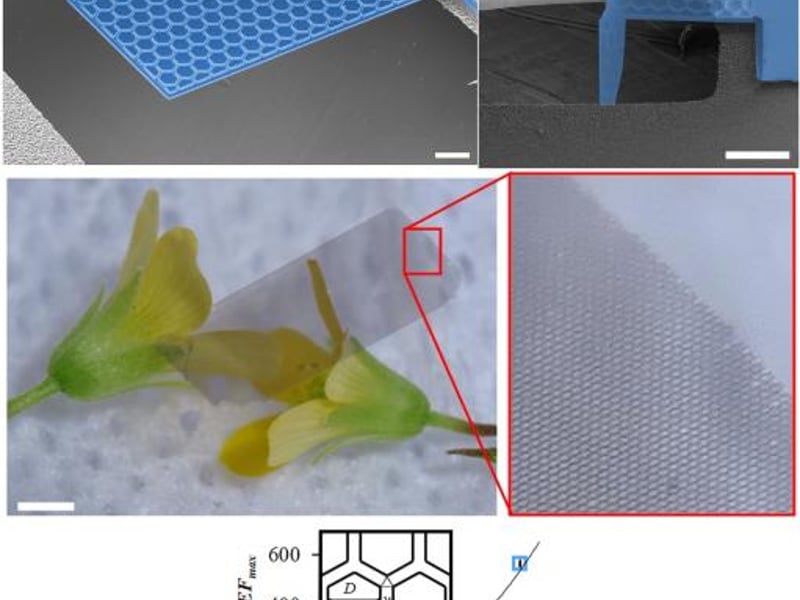
Plate Mechanical Metamaterials
I. Bargatin & P. K. Purohit (Seed 5)

Helium Conservation in the Property Measurement Facility (SEF)
J. M. Kikkawa
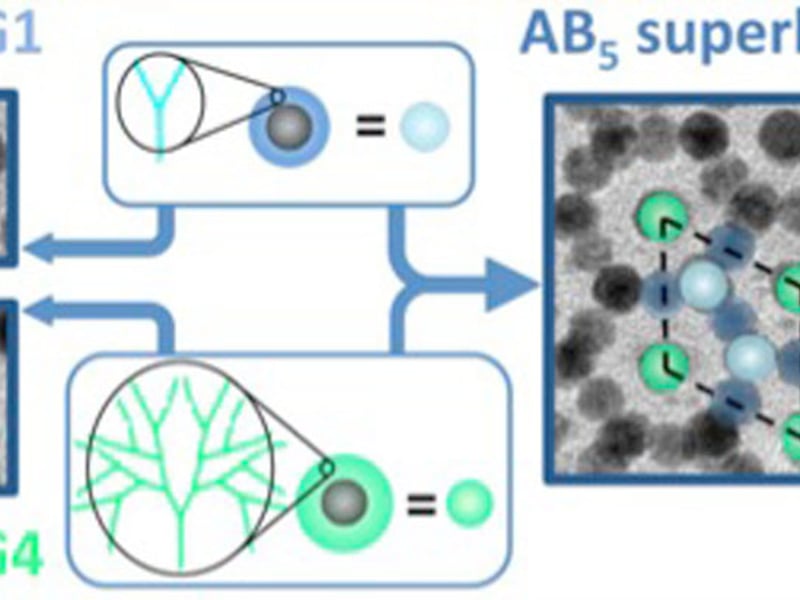
Dendrimer-Nanocrystal Building Blocks
L. Hough, C. B. Murray, & B. Donnio (IRG-4)
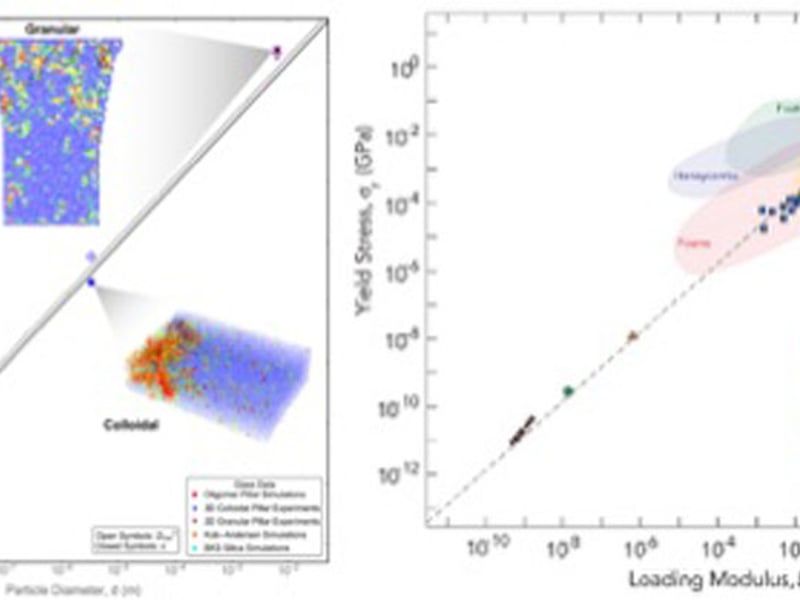
Universality of Microscopic Structure and Macroscopic Mechanical Response in Disordered Packings Across Length Scales
P. E. Arratia, R. W. Carpick, D. J. Durian, D. S. Gianola, D. Lee, A. J. Liu, R. Riggleman, A. G. Yodh (IRG-3)
Video Archives of Outreach Presentations
A. R. McGhie & M. W. Licurse

Top Chefs at the MRSEC
Michael Brenner and David Weitz (School of Engineering and Dept. of Physics)
Showing 531 to 540 of 1396