Highlights
May 15, 2024
University of California, Santa Barbara
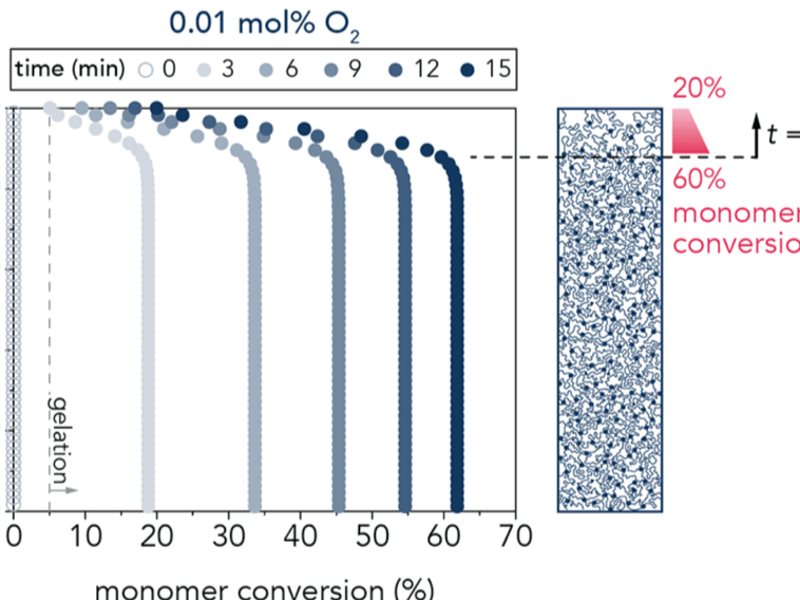
Superlubricious Hydrogels from Oxidation Gradients
Chau, Edwards, Helgeson, Pitenis - University of California, Santa Barbara
Hydrogels are hydrated three-dimensional networksof hydrophilic polymers that are commonly used in the biomedical industry due to their mechanical and structural tunability, biocompatibility, and similar water content to biological tissues.
May 15, 2024
University of California, Santa Barbara
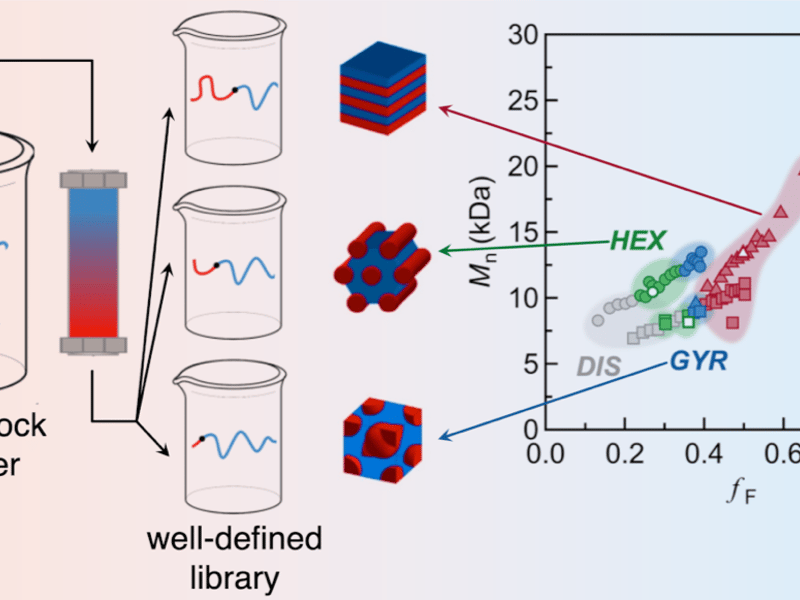
Rapid Generation and Screening of Complex Polymer Morphologies
Murphy, Skala, Kottage, Kohl, Li, Zhang, Hawker, Bates - University of California, Santa Barbara
Block copolymers, with their complex morphologies, are widely used in many applications. A grand challenge associated with these materials is accelerating their design and discovery.
UC Santa Barbara MRSEC researchers have developed a versatile and efficient strategy by rapidly building expansive, high-quality, and detailed block copolymer libraries through a combination of controlled polymerization and chromatographic separation. X-ray scattering studies aid in screening block copolymer morphology.
May 15, 2024
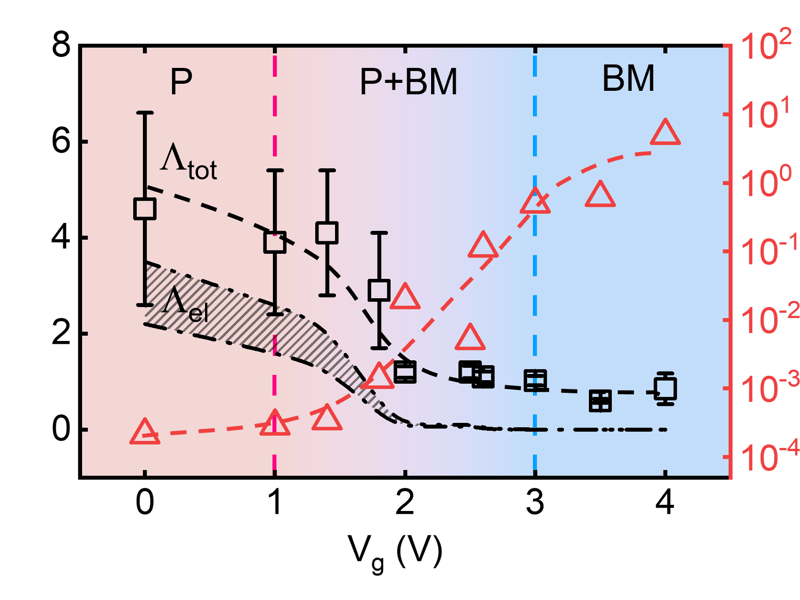
UMN Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
Record Voltage-Based Tuning of Thermal Conductivity in La0.5Sr0.5CoO3-d
A team from IRG-1, working with collaborators at Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Utah, have demonstrated continuous room-temperature electrical tuning of the thermal conductivity of La0.5Sr0.5CoO3-d by a factor of more than five (a record for a single-step process) via ion-gel gating. Application of a gate voltage in these devices drives a transformation from a metallic perovskite phase to an insulating brownmillerite phase via the formation and migration of oxygen vacancies, realizing the record range of measured thermal conductivities.
May 15, 2024
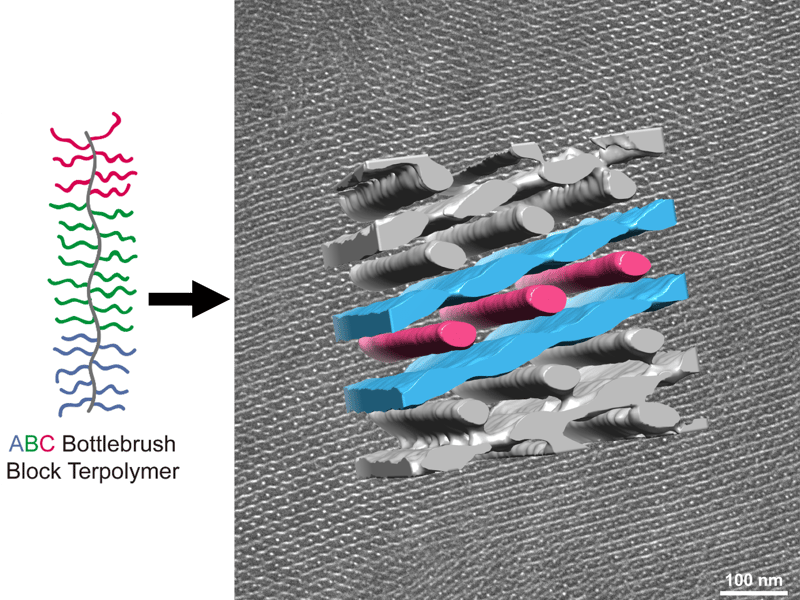
UMN Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
Unprecedented Nanoscale Morphology in Self-Assembled Bottlebrush Block Polymers
Soft materials known as molecular bottlebrush block polymers comprise a polymer backbone with densely grafted polymer side chains. These materials have attracted much attention for their ability to self-assemble into ordered structures with relatively large periodicities (over 50 nm), which are rarely achieved with simpler linear polymers. However, only self-assembly into lamellar and cylindrical phases has been reported in diblock bottlebrush materials.
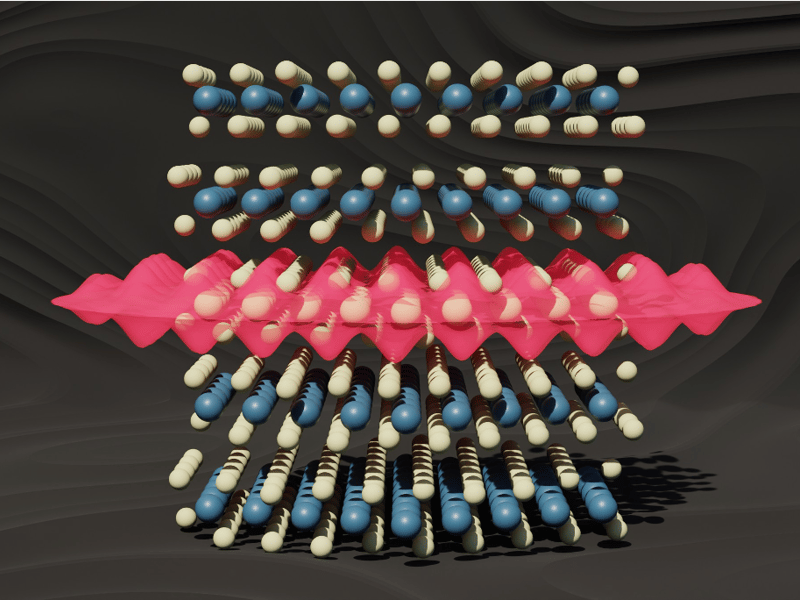
May 15, 2024
Big Idea: Quantum Leap
Endotaxial stabilization of 2D charge density waves with long-range order
Rather than the typical approach of exfoliating and peeling off individual atomic layers to make a 2D material, the researchers grew the 2D material inside of another matrix. The work has dubbed this new class of materials "endotaxial" from the Greek roots "endo", meaning within, and "taxis", meaning in an ordered manner.
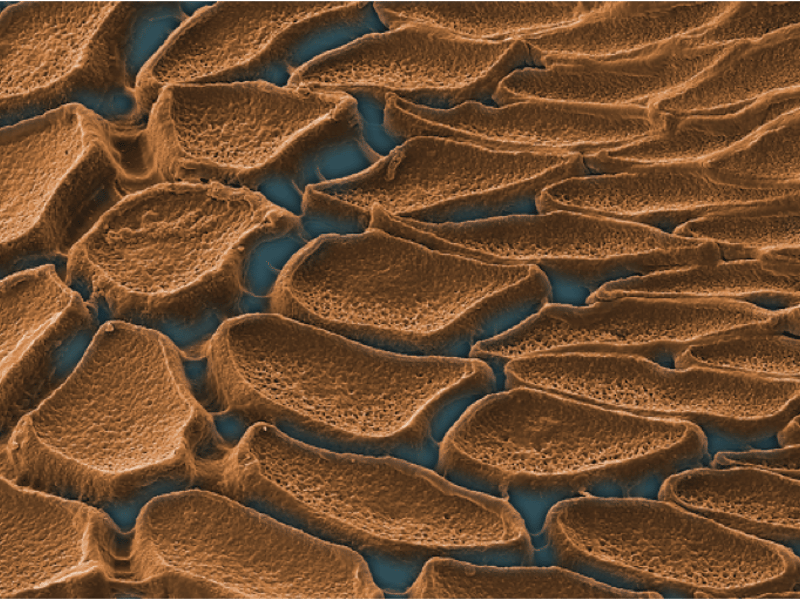
May 15, 2024
Big Idea: Recyclable Plastics and Alternative Materials
Thermomechanical Properties of Squid Sucker Proteins
This article studies the reversible structure and mechanical properties of a biological dynamic polymer network. This biological material based on structural protein polymers has a glass transition at 35 °C, causing a reversible thermomechanical transition and a change in modulus spanning several orders of magnitudes.
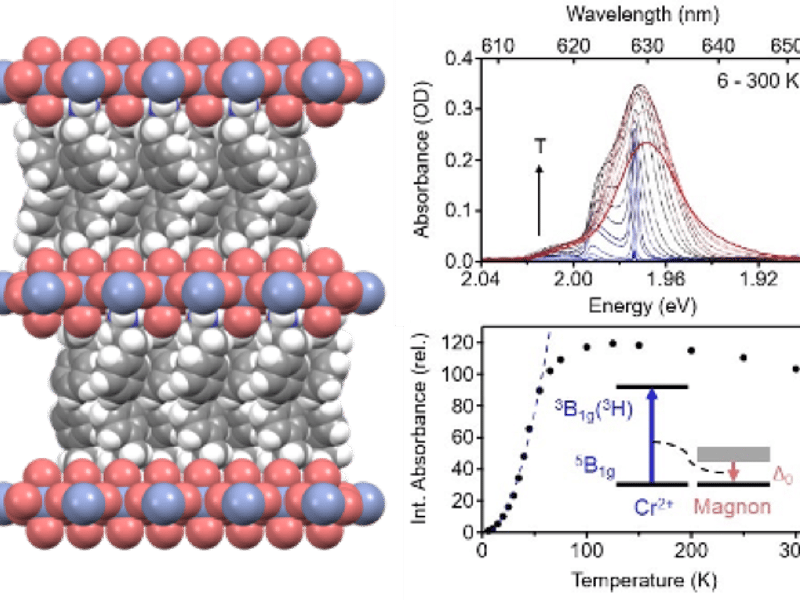
May 15, 2024
University of Washington
MEM-C IRG-1: Spin-Photonic Coupling in a Ferromagnetic Hybrid Layered Perovskite, (PEA)2CrCl4
The Cr2+-based compounds, A2CrX4, where A = M+ (e.g., K+, Cs+, Rb+) or RNH3+ (e.g., MeNH3+) and X = Cl-, Br-, are an underexplored family of lead-free layered metal-halide perovskites. These compounds attracted a great deal of interest in the 1970s and 1980s after their "transparent ferromagnetism" was discovered, but they have received virtually no attention since, perhaps because they are extremely unstable in air. Further investigation into their chemistry and properties is warranted.

May 15, 2024
University of Washington
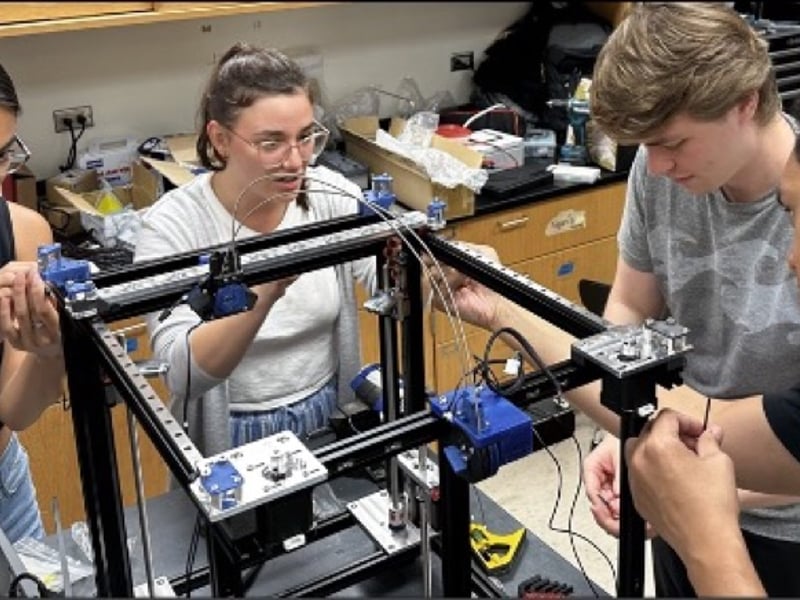
MEM-C SEED: Expanding Data Automation Using a Jubilee Robotic Platform
UW Chemical Engineering Prof. Lilo Pozzo’s ‘23/’24 Seed project aims to serve the materials community by advancing AI-driven experimentation and analysis for broad adoption and acceleration of materials research. Pozzo has engaged in highly collaborative projects to advance self-driving laboratory (SDL) technologies and to help others adopt them for their own workflows.
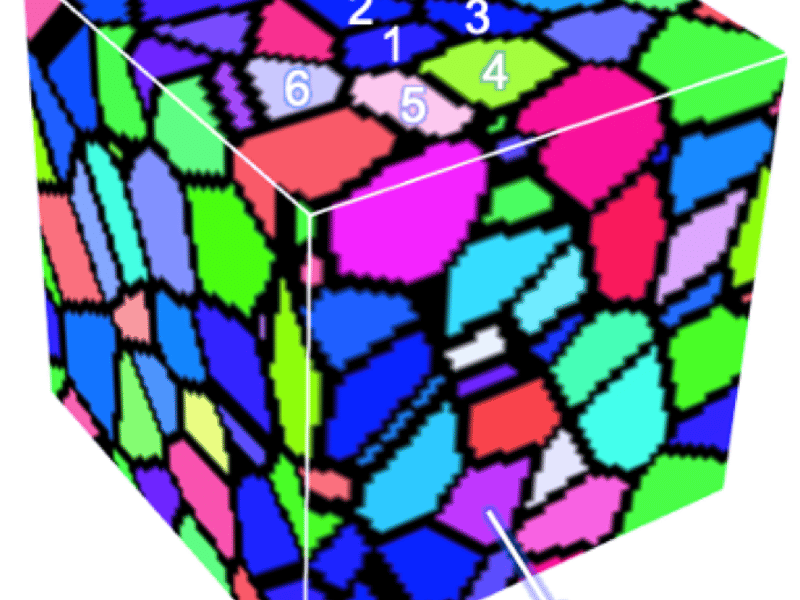
May 15, 2024
Big Idea: Harnessing the Data Revolution, Machine Learning / Artificial Intelligence
Graph Machine Learning for Polycrystals
Wisconsin MRSEC researchers have leveraged the power of machine learning to tame the complexity of polycrystalline materials and predict their properties. They have developed a graph neural network approach that predicts materials properties with >98% accuracy 90,000 times faster than competing methods. They applied this model to predict magnetostriction, which quantifies the size change of a material induced by a magnetic field.
May 15, 2024
University of Wisconsin - Madison
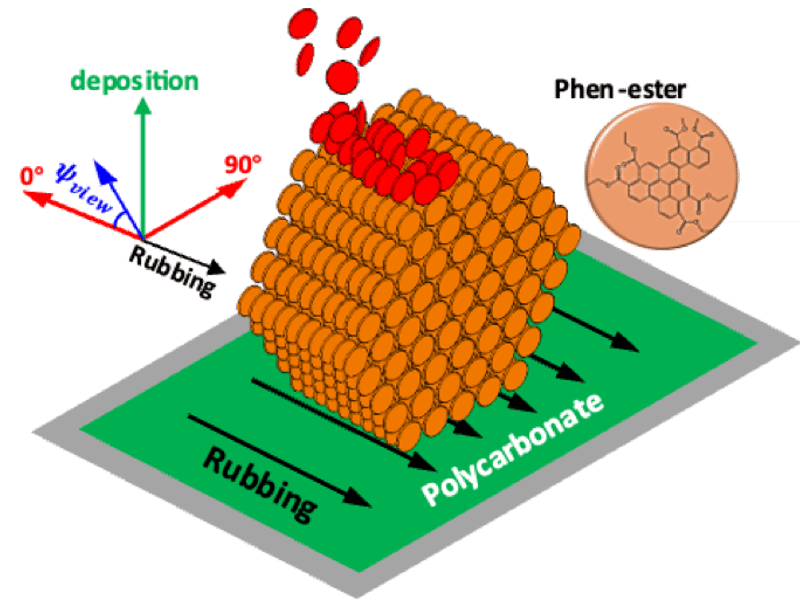
Biaxially-aligned Glasses of Organic Semiconductors
Researchers in the Wisconsin MRSEC have shown that depositing onto an alignment substrate creates better glass films that are anisotropic biaxially, meaning they are aligned in the plane of the substrate as well as out of plane. The in-plane orientation of the molecules affect how they interact with light and conduct electricity. In general, more alignment is better for applications ranging from flexible transistors to OLEDs to organic photovoltaics.
Showing 81 to 90 of 1396